Terminologies TV :termes importants à connaître
Vous est-il déjà arrivé de parler à quelqu'un de la technologie de la télévision et qu'il mentionne un mot que vous ne connaissez pas et que vous vous trompez ? Avez-vous déjà rencontré un terme qui n'a pas beaucoup de sens en lisant un guide pour acheter le meilleur téléviseur ? Il existe plusieurs mots ou terminologies que nous rencontrons en lisant ou en discutant de la télévision. Cela devient particulièrement irritant lorsque vous devez acheter un téléviseur et que vous êtes confronté à trop de terminologies inconnues. Pour vous aider à résoudre ce problème et vous familiariser avec ces termes peu familiers, nous avons préparé une liste de terminologies TV.
Ici, nous allons discuter et essayer d'expliquer ces terminologies difficiles avec des mots simples.
- Format :
Le format d'image fait référence au rapport largeur/hauteur d'un écran de télévision et définit la forme du téléviseur. Il existe différents rapports d'aspect pour les téléviseurs et cela varie en fonction de la résolution. Certains rapports d'aspect ne conviennent qu'à certaines résolutions, conçus pour vous offrir la meilleure qualité d'image sans distorsion ni étirement, et pour éviter tout espace vide sur n'importe quel côté de l'image. Le format d'image le plus courant pour les téléviseurs aujourd'hui est 16:9. Lorsque le contenu et le format d'image de votre téléviseur ne correspondent pas, des barres noires apparaissent dans l'espace vide (les barres verticales sont appelées colonnes et les barres horizontales sont appelées boîtes aux lettres). Sur certains téléviseurs, vous pouvez résoudre ce problème en zoomant sur l'image, en recadrant l'image ou en utilisant un mélange des deux.
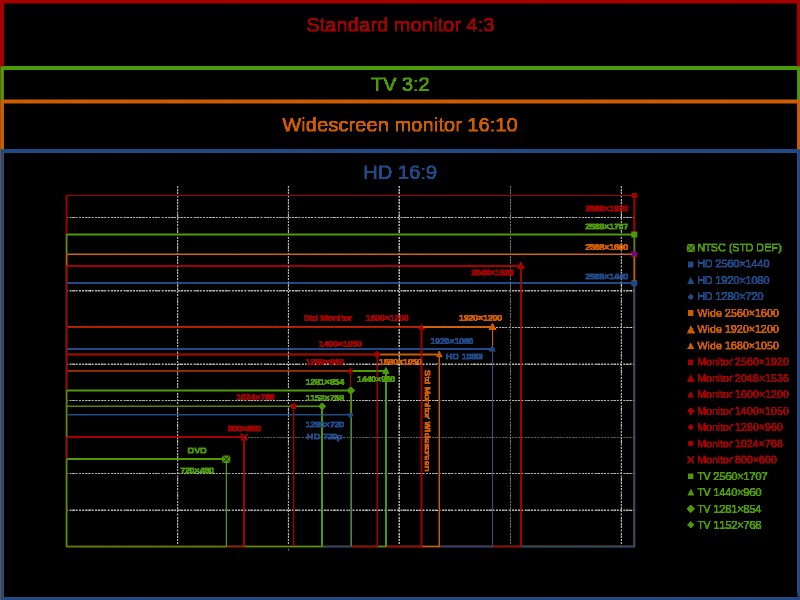
Crédit image :Wikimedia Commons - Lunette :
En termes simples, la lunette désigne le cadre autour de l'écran ou la forme structurelle que vous pouvez voir à l'avant du téléviseur, à l'exception de son écran. Bien qu'ils soient importants pour l'intégrité structurelle, ils affectent l'expérience visuelle car ils couvrent une partie de l'écran de tous les côtés. La plupart des téléviseurs sont sans cadre de nos jours, ce qui signifie un cadre très fin sur l'écran, permettant à l'écran du téléviseur d'être plus grand sans avoir à augmenter la taille du téléviseur.

Crédit image :trustedreviews.com - Taux de contraste :
Le rapport de contraste d'un téléviseur désigne le rapport entre ses réglages les plus clairs et les plus sombres. Le rapport de contraste d'un téléviseur est l'une des caractéristiques importantes qui aident à décider de la qualité d'un téléviseur. Cela affecte les images que vous voyez à l'écran et le rapport de contraste est affecté par un certain nombre de facteurs tels que la réflectance de l'écran, l'éclairage de la pièce, les paramètres de l'image et le contenu affiché lui-même. Le rapport de contraste d'un téléviseur peut être mesuré sur deux bases, à savoir le rapport de contraste natif et dynamique. Le rapport de contraste natif, également appelé rapport de contraste statique ou à l'écran, représente le rôle du panneau TV tandis que le rapport de contraste dynamique consiste à faire fluctuer les rétroéclairages LED installés à l'arrière de l'écran pour un meilleur contraste. Les fabricants de téléviseurs utilisent différentes méthodes pour mesurer le rapport de contraste, ce qui rend cette fonctionnalité inutile lors de l'achat d'un nouveau téléviseur. Mais le rapport de contraste est très pratique pour comparer différents téléviseurs avant de décider lequel acheter.
- CRT :
CRT ou Cathode Ray Tube (également connu sous le nom de tube image) dans CRT TV est un tube à vide où les images que nous voyons à la télévision sont créées. L'écran phosphorescent ou fluorescent est balayé par des faisceaux d'électrons pour former les images. Les faisceaux se déplacent d'avant en arrière, éclairant les lignes de points de phosphore à l'intérieur du tube de verre, dessinant plusieurs lignes sur l'écran et créant des images ou des images pour le téléviseur. Désormais obsolètes, les téléviseurs Direct avaient un grand tube image à l'intérieur tandis que les téléviseurs CRT à projection arrière et avant ont trois tubes image pour les couleurs primaires, c'est-à-dire le vert, le rouge et le bleu.
- Port Ethernet :
Le port Ethernet de votre téléviseur vous permet de connecter votre téléviseur à Internet à l'aide d'un câble. Tout ce que vous avez à faire est de connecter une extrémité du câble Ethernet au port et l'autre extrémité à votre routeur pour diffuser des émissions et des films Internet sur votre téléviseur. Il fournit une connexion plus stable avec une latence plus faible et une meilleure vitesse.
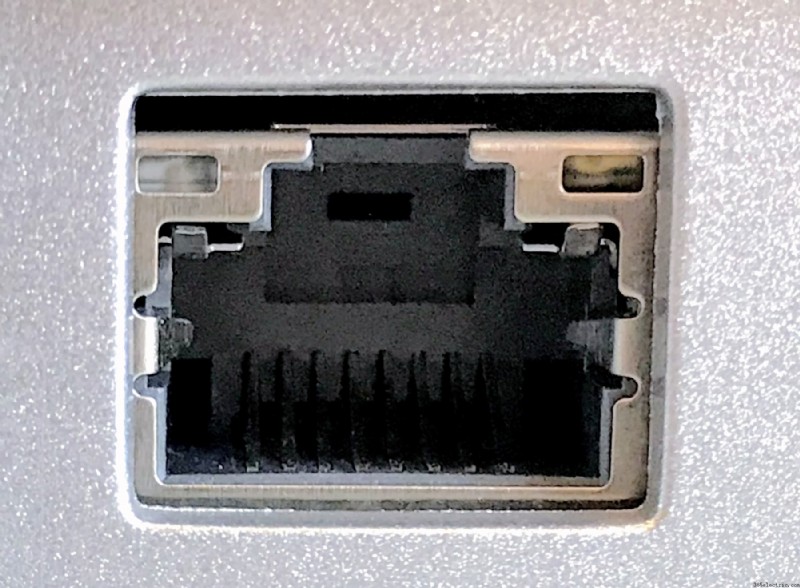
Image credit:Wikimedia Commons - Frame rate:
Frame rate means the speed at which the consecutive image slides are displayed. It is usually expressed as frames per second or fps. Higher the frame rate, the higher the number of frames used and it will mean more bandwidth for streaming the video. High frame rates have become popular these days as they capture a higher number of images per second which results in a smoother video. The high-definition videos often have a frame rate of 60 fps.
- HDMI:
HDMI or High-Definition Multimedia Interface is a digital interface that helps in transferring high-definition audio and video signals through a cable. It can be used to transfer a video quality of up to 4k Ultra HD resolution, 3D videos, and multichannel surround sound in high quality.
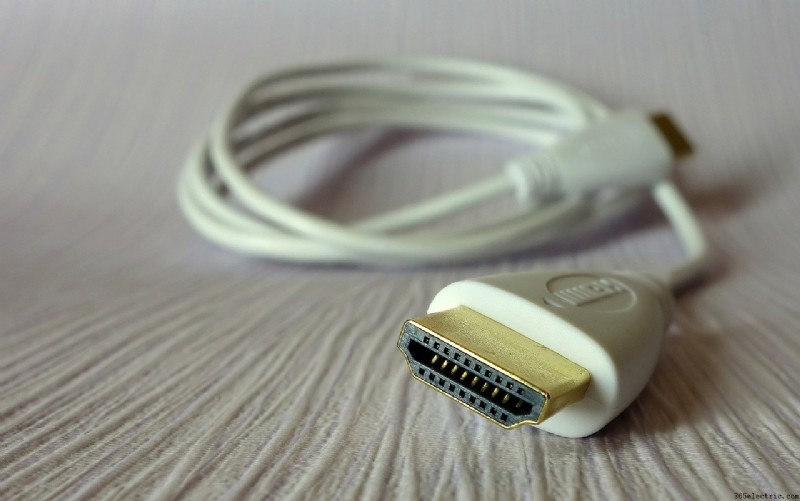

Image credit:Pixabay - HDR:
HDR or High Dynamic Range is a feature that affects the TV’s contrast ratio and color accuracy and helps make the pictures look more realistic. It is almost a must-have feature for TVs these days due to the detail it provides to the images through the right color balancing. Almost all the mid-range to high-range TVs have this feature and even most of the movies and shows on TVs are HDR now. Though, one thing to remember here is that TV HDR and photo HDR are not the same. These are two different concepts with the same name, making almost everyone confused.
- kHz:
KiloHertz or kHz represents a thousand frequency cycles per second. In simple words, it is a measurement of frequency i.e., the number of times a wave repeats itself in a second. 1 kHz means 1000 times per second. It is also used to measure the signal bandwidth, digital as well as analog. In the case of TVs, higher kHz means better sound quality.
- OLED:
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) is a display technology that uses thin organic films between the two electrodes to produce light with the help of electricity. The organic process of creating the images on the screen with the light produced is called electroluminescence, meaning that the display is self-illuminating and does not need any backlight. OLED TV panels are lighter and thinner in comparison to LCD TVs and also help in saving energy.
- Over the top services:
Over-the-top services or OTT services are streaming services that offer media content directly to the viewers through the internet. These services are provided by bypassing the traditional platforms like broadcast, cable, and satellite TV. OTT content mostly includes shows and movies that you watch on phone, tablet, or laptop and can be streamed on an internet-connected TV like Smart TV. Some of the OTT service providers are Netflix, Amazon Prime, Disney+, etc.
- Pixelation:
Pixelation means stretching of the pixels beyond their original size and it is usually caused due to a weak signal. When the signal is poor, sometimes the TV fails to get the complete data or any data at all during the transmission. This leads to the formation of an incomplete image where some pixels are either missing or too stretched.

Image credit:Flickr - Plasma:
Plasma is a screen technology that was used in making the first flat display panels for large TVs and was a dominant TV technology just a few years back. A plasma display panel has small cells (like tiny CFLs) which are coated with red, green, or blue phosphorus. The cells also have neon or xenon gas inside them which creates invisible ultraviolet lights. These lights are then converted into the red, green, or blue light that we see on the screen via the light emitted by these cells. When we compare plasma with LEDs, plasma TVs are better as they have better picture quality and viewing angles. But, it also has many disadvantages, one of them being that it is now outdated technology. Also, the little cells or gas packets behind the panels can cause burn-in on your screen i.e. burn the images in your screen to show them even when your TV is switched off. They are also available only in larger sizes and are not that energy-efficient.
- Quantum Dots:
Quantum dots can be defined as nanocrystals that absorb light and convert its wavelength. These are used in QLED TVs where they are placed in front of a normal LED backlight in a layer. All these crystals emit individual colors of their own based on their size. Though the light emitted by these quantum dots still goes through the filter, the lights are highly pure that helps in expanding the TV’s color range, and creates more intense and deeper colors. These dots also enhance the light efficiency of the TV and thus produce brighter pictures.
- Resolution:
Resolution can be defined as the number of pixels or dots that create the pictures that you see on your TV screen. It is denoted as the number of pixels in one horizontal line by the number of pixels present in one vertical line. Higher the number of pixels, the higher the resolution, and the better the picture quality. There are four resolutions commonly used in TVs these days and each of them has a name as which are 1280×780 (HD), 1920×1080 (Full HD), 3840×2160 (Ultra HD/4k), and 7620×4380 (Ultra HD/8k). TV resolution is usually indicated in two ways, for example, 1080i or 1080p resolution. When you have both the options in front of you, choose the latter one. The “i” means interlaced and the “p” means progressive. The difference between both is that the interlaced videos display every alternate horizontal pixel line while the progressive lines display every horizontal pixel line, making the picture quality of progressive videos better than its counterpart.
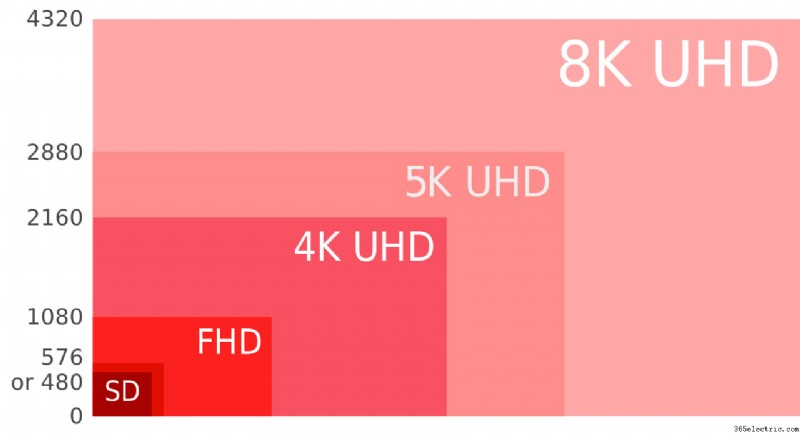
Image credit:Wikimedia Commons - Refresh Rate:
Refresh rate is defined as the number of times your TV screen refreshes itself in a second. It is denoted by Hertz or Hz. A higher refresh rate usually means smoother motion on the screen, but not always. However, the refresh rate should not be confused with the frame rate (fps). Frame rate represents the number of frames displayed on the screen per second. For clear motion and images, make sure that the refresh rate and frame rate of your TV match or in other words are the same, for example, if the refresh rate is 60 Hz, the frame rate should be 60 fps.
- Soap Opera Effect:
Soap Opera Effect is a visual effect created by most of the TVs by default. It involves creating additional frames in between the already existing ones by motion interpolation process to make the pictures look more crisp and realistic. It shows the content on your screen at a refresh rate that is higher than the original source of the content. Though it comes in handy when there is an action scene on the screen like sports events, it also wipes the normal cinematic blur from any fast-moving object on the screen. Removal of the blur hinders the ideal cinematic experience and makes the pictures more animated, giving them a soap opera effect, that is why the name. You can turn it off on your TV from the settings. This visual effect is also known as Enhanced Motion, Smooth Motion, or Auto Motion Plus, which are just marketing strategies.
- Viewing Angle:
Viewing angle means the maximum angle at which you can watch your TV screen comfortably without any color shift or loss of brightness. The ideal position is directly in front of the TV screen and at eye level. As per LCD/ LED TV manufacturers, the best viewing angle for your TV is 88 or more. At this angle, you get clear and well-defined images with the best color accuracy.
- UHD:
UHD or Ultra High Definition represents a higher resolution for the TV display. UHD TVs come in 4k (3840×2160) and 8k (7620×4380). These resolutions have a higher number of pixels than a normal HD TV. UHD displays are used in larger TVs, so you can enjoy a clearer and crisp image even while sitting relatively closer to the TV.
- Upscaling:
Upscaling basically means stretching an image with a lower resolution to fit on a larger display. In this, the pixels of the image with low resolution are copied and are repeated to fill up the display of a higher resolution. Almost every TV comes with upscaling now. In the case of HD TVs, the upscaling process makes the lower resolution images look bigger and better on the screen by increasing the pixel count.
