Caissons de subwoofer, plus qu'un simple boîtier
 Pendant des décennies, il y a eu discussion après discussion pour savoir lequel des différents caissons de subwoofer est "le meilleur" et pourquoi. Voyons pourquoi nous avons besoin d'un boîtier de subwoofer et comment les trois styles populaires (scellé, ventilé et passe-bande) diffèrent dans leur conception et leurs performances.
Pendant des décennies, il y a eu discussion après discussion pour savoir lequel des différents caissons de subwoofer est "le meilleur" et pourquoi. Voyons pourquoi nous avons besoin d'un boîtier de subwoofer et comment les trois styles populaires (scellé, ventilé et passe-bande) diffèrent dans leur conception et leurs performances.
Gestion des contre-ondes
Si vous deviez brancher n'importe quel haut-parleur à un amplificateur, le tenir dans votre main et y jouer de la musique, vous constateriez que vous n'entendez aucune basse. En effet, le son provenant de l'avant de l'enceinte annule le son provenant de l'arrière. Nous avons besoin d'un moyen d'empêcher le son provenant de l'arrière du cône du haut-parleur d'interférer avec le son provenant de l'avant. Si vous deviez couper un trou au milieu d'un grand morceau de bois plat et y monter le haut-parleur, vous entendrez beaucoup plus de basses. En fait, jusqu'à ce que la demi-longueur d'onde des basses fréquences devienne plus longue que les dimensions du morceau de bois, vous obtiendrez de très bonnes basses solides. Si nous plaçons une enceinte dans une enceinte hermétique, aucun son provenant de l'arrière n'interfère avec le son provenant de l'avant.
Gestion de puissance
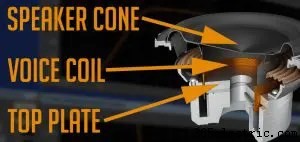
La capacité d'un haut-parleur à utiliser la puissance produite par un amplificateur est limitée par deux critères :la distance à laquelle le cône du haut-parleur peut se déplacer et la quantité de chaleur que la bobine acoustique du haut-parleur peut supporter. Les limites de gestion de la puissance thermique reposent principalement sur la conception d'un haut-parleur - la taille de la bobine mobile, la manière dont le flux d'air est géré autour de la bobine mobile et la proximité des composants fixes de l'ensemble moteur par rapport à la bobine mobile sont les principaux facteurs contributifs . Les contraintes d'excursion limitée font également partie de la conception de l'enceinte :la longueur de l'enroulement de la bobine mobile, la hauteur de la plaque supérieure et le débattement de suspension disponible sont les facteurs clés.
Excursion
Lorsqu'il s'agit de reproduire des basses, un haut-parleur doit se déplacer quatre fois plus loin chaque fois que la fréquence d'entrée est divisée par deux. Par exemple, un haut-parleur se déplaçant de 0,125 pouce à 100 Hz doit se déplacer de 0,5 pouce pour reproduire le même niveau de sortie à 50 Hz et de 2 pouces à 20 Hz. Vous pouvez voir que, pour les fréquences les plus basses, les limitations d'excursion du cône sont importantes - très peu de haut-parleurs peuvent se déplacer de 2 pouces sans distorsion significative.
Lorsque nous mettons un haut-parleur dans une enceinte, la combinaison de l'enceinte et du haut-parleur crée un filtre passe-haut. Nous diminuons efficacement la sortie basse fréquence du haut-parleur. Pourquoi voudrions-nous faire cela? L'avantage d'une enceinte est que nous pouvons contrôler le mouvement du cône du haut-parleur. L'examen d'une simple enceinte de suspension acoustique (également appelée enceinte étanche) sera l'illustration la plus simple de cette explication.
Conformité
Each and every speaker – from the biggest of subwoofers to the smallest of tweeters – has a springiness to the cone. We call this the compliance. We measure compliance by comparing it to a volume of air with the equivalent springiness. We call this characteristic of the speaker Vas. In general terms, a speaker with a very small Vas specification has a tight suspension, and a speaker with a large Vas has a softer suspension. There is a lot more to it than that, but for the discussion of enclosure features and benefits, that’s all we need to get into for now.
 When we put a speaker in an enclosure, we stiffen the suspension. When you push in on the speaker cone, you are pushing against the speaker’s suspension (which wants to center the cone) and you are trying to pressurize the air in the enclosure. When the cone tries to move outward from rest, you are putting the air in the into a vacuum state – it wants to pull the cone back to its resting position. We do sacrifice low-frequency output, but we gain significant power handling and control over the motion of the speaker cone. For the latter, the combination of the air in the enclosure and the speaker suspension helps to stop the speaker cone from moving once an electrical signal starts it in motion.
When we put a speaker in an enclosure, we stiffen the suspension. When you push in on the speaker cone, you are pushing against the speaker’s suspension (which wants to center the cone) and you are trying to pressurize the air in the enclosure. When the cone tries to move outward from rest, you are putting the air in the into a vacuum state – it wants to pull the cone back to its resting position. We do sacrifice low-frequency output, but we gain significant power handling and control over the motion of the speaker cone. For the latter, the combination of the air in the enclosure and the speaker suspension helps to stop the speaker cone from moving once an electrical signal starts it in motion.
Think of it like a shock absorber on a vehicle. You can see that having an enclosure is critical.
Acoustic Suspension Subwoofer Enclosures
The simplest of enclosures is called an acoustic suspension or sealed enclosure. In these enclosures, we are putting the speaker into an airtight box. When we put a speaker in an enclosure, the system resonates at a specific frequency that – we call this Fc. Below that frequency, the output is reduced at a rate of -12 dB per octave. If the system has a resonant frequency of 50 Hz, the output will be 12 dB quieter at 25 Hz.
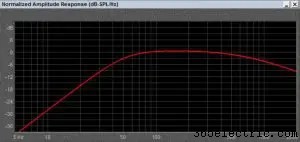
Acoustic suspension enclosures are amongst the smallest of the different enclosures we will discuss. They are also the easiest to construct, and most forgiving regarding calculation error. If you combine the roll-off of the enclosure and speaker system with the increase in efficiency you get from the relatively small air volume of the vehicle interior (often called transfer function or cabin gain), you can get a very flat in-car response with good infrasonic output. Bass from an acoustic suspension enclosure is very tight and controlled, thanks to excellent transient response.
There is a down side. If you are looking for loud bass, then you need a driver that has a lot of excursion capability, and you need a reasonable amount of power to move the speaker cone back and forth to get the level of output you want. There is another drawback that isn’t talked about as much, and that is distortion. As a speaker increases in excursion, the amount of distortion it creates increases. Likewise, distortion increases near the resonant frequency of the speaker. So, what can you do?
Bass Reflex Subwoofer Enclosures
A bass reflex (also known as ported or vented) enclosure uses a vent to increase low-frequency output by making use of the speakers back-wave energy. The vent, often a round tube or sometimes a rectangular slot, has an area and a length. The specific area and length of the vent and their relationship to the total volume of the enclosure cause the column of air in the vent to resonate at a specific frequency when excited by the speaker. We typically tune bass reflex enclosures quite low to emphasize the bottom octave or so of the audible frequency range. They can be tuned higher to increase efficiency for high-SPL applications. There is always a sacrifice, though – when we tune the enclosure higher, we sacrifice low-frequency performance.
Bass reflex enclosures are typically larger than sealed enclosures. There is no hard-and-fast rule to associate with the size relationship, but 25–50% large is common. The trade-off for that extra volume is two-fold – more efficiency in the tuning frequency and more power handling, at some frequencies.
When the subwoofer used in a bass-reflex subwoofer enclosure produces frequencies around the resonant frequency of the vent/enclosure combination, the driver excursion is reduced to almost nothing and all the “work” is done by the vent. Put more succinctly, around the tuning frequency, most of the music is being produced by the vent. The benefit to this is that power-handling problems caused by cone excursion limitations are dramatically increased. Since the cone is barely moving, very high sound pressure levels can be achieved. Around the tuning frequency, power handling is limited by the thermal capabilities of the subwoofer.
As we mentioned earlier, one factor that contributes to loudspeaker distortion is cone excursion. With a bass reflex enclosure, the driver moves significantly less than with an acoustic suspension enclosure design. As long as the vent itself has enough area and a smooth transition at both openings, the distortion produced by a properly designed bass reflex enclosure can be impressively small.
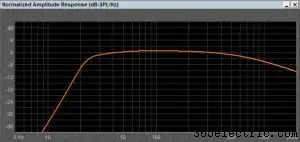
Nothing is free, is it? A factor in deciding to use a bass reflex design is how fast the output decreases below the tuning frequency. Where an acoustic suspension enclosure rolls off at -12 dB per octave, a bass reflex enclosure rolls off at 24 dB per octave. Below the tuning frequency, the vent acts more and more like a hole in the enclosure, offering increasingly less back pressure as frequency decreases. Designing for, and managing, driver excursion is a fundamental part of bass reflex enclosure design.
Bandpass Subwoofer Enclosures
We will quickly touch on bandpass enclosures to wrap up this article. There are several different designs for bandpass enclosures. Some use a sealed enclosure, and some a vented one. Independent of whether the rear chamber is sealed or vented, the output of the subwoofer plays into a vented enclosure. This enclosure acts as a low-pass filter. Why would we want to design a bandpass enclosure?
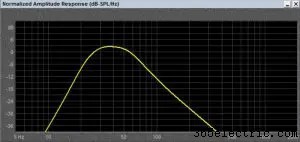
First and foremost, all of the output of the enclosure is produced by the vent or vents. This allows a creative designer to build an enclosure in the trunk of a vehicle and have the vent opening play through the rear parcel shelf. There have been some amazing bandpass enclosures build in the front storage area of mid- or rear-engine vehicles. The vent allows the bass to enter the interior of the vehicle. Bandpass enclosures can also offer impressive gains in efficiency over acoustic suspension and bass reflex enclosures, but they do so at the sacrifice of bandwidth and enclosure volume.
A bandpass enclosure has two resonant frequencies – one for each of the enclosures. The resultant management of cone excursion can allow a great deal of bass to be produced from limited excursion drivers. While the speaker cone itself does not move a great deal, the amount of work done by the motor assembly is still significant. You are still putting power into the speaker, and work is being done. Because the front chamber of the enclosure acts as a filter, it can also be very difficult to hear when the speaker is distorting.
Regarding the complexity of design, and forgiveness of construction error, bandpass enclosures are the most complicated to execute perfectly. Unlike an acoustic suspension or bass-reflex design, bandpass enclosure designs must be tailored exactly to the speaker they are being used with. Never trust the concept of a “generic” bandpass enclosure.
Lastly, because a bandpass enclosure includes an acoustic low-pass filter, it has to be used with good-quality, appropriately sized midbass drivers. If not, the bass can sound lost or disconnected relative to the rest of the music.
For More Details On Subwoofer Enclosures, Visit Your Local Specialist
As you can see, there are many ways to install a subwoofer – or any speaker, for that matter. Navigating the available space in the vehicle, as well as different speaker sizes and designs, can be tricky. The design and construction of an enclosure can be complex, especially when complex shapes are involved. Visit your local car audio specialist retailer to explore different enclosure options for your vehicle.
